Surface Guided Radiation Therapy (SGRT) is a rapidly growing technique that uses stereo vision technology to track patients’ surface in 3D, for both setup and motion management during radiotherapy. Surface Guided Radiation Therapy can be used for many types of radiation therapy. There are numerous publications that support its use in the treatment of breast, brain, head and neck cancer, sarcoma, and other conditions.
Introduction to Surface Guided Radiation Therapy (SGRT)
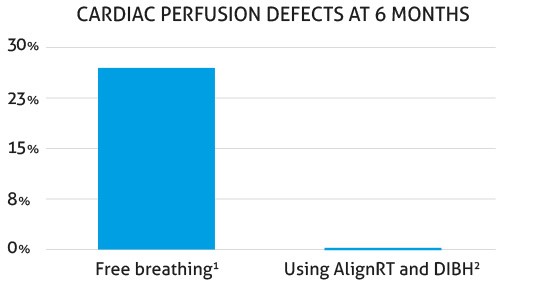
A recent study 3 showed that AlignRT + DIBH effectively prevented radiation-induced abnormalities in blood flow to the heart. Of the breast cancer patients treated, 0% showed these abnormalities after six months. This compares to a previous study without AlignRT or DIBH, where 27% of patients showed new abnormalities in blood flow to the heart 6 months after radiation therapy 4 . Additionally, there are more than 10 publications that demonstrate the accuracy of the technique.
Get in touch
Vision RT’s family of SGRT solutions guide radiation therapy for better patient care at every step: sim, planning and treatment.
Whether you’re looking for a quote, a product demo (virtual or in-person) or just more information, please get in touch:
1. Darby et al. Risk of Ischemic Heart Disease in Women after Radiotherapy for Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med 2013; 368:987-998
2. Gierga et al. A Voluntary Breath-Hold Treatment Technique for the Left Breast With Unfavorable Cardiac Anatomy Using Surface Imaging. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Dec 1;84(5):e663-8
3. Zagar et al. Prospective Assessment of Deep Inspiration Breath Hold to Prevent Radiation Associated Cardiac Perfusion Defects in Patients With Left-Sided Breast Cancer J Appl Clin Med Phys. 2015 ;93:3S 2027
4. Marks, L. B. et al. The incidence and functional consequences of RT‑associated cardiac perfusion defects. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 63, 214–223 (2005)
5. Pan et al. Frameless, real-time, surface imaging-guided radiosurgery: clinical outcomes for brain metastases. Neurosurgery. 2012 Oct;71(4):844-51.
6. Pham et al. Frameless, real-time, surface imaging-guided radiosurgery: update on clinical outcomes for brain metastases. Trans. Cancer Res, 3, 4, 351-357, August, 2014.



