Surface Guidance for Better Radiation Therapy Planning
Plans with lower organ-at-risk (OAR) dose, including non-coplanar VMAT plans, have historically been more difficult to plan and have taken longer to deliver than simple VMAT arcs.
MapRT helps increase the therapeutic ratio of treatment plans, making advanced and non-coplanar planning simple and safe1-26:
-
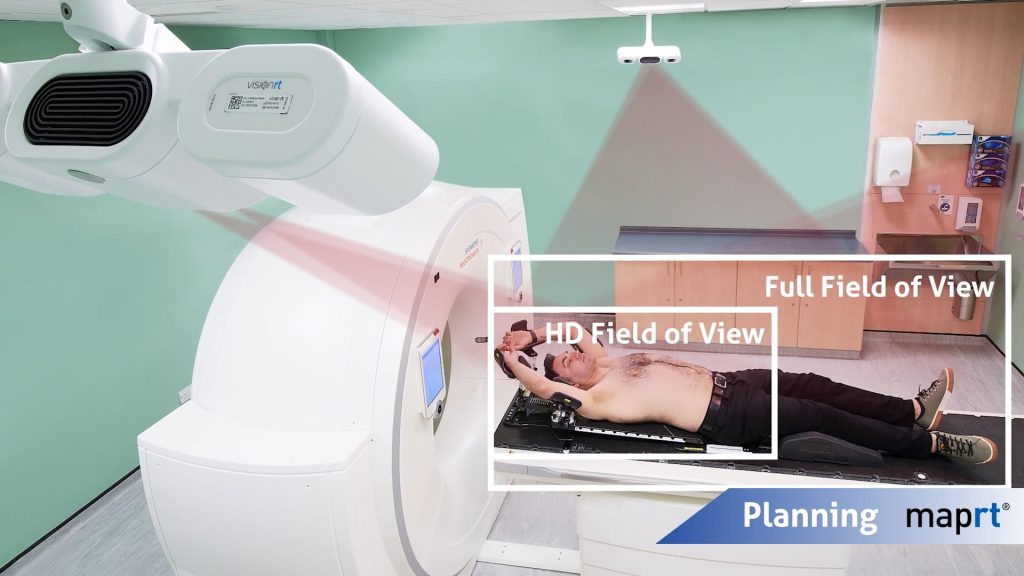
- Two lateral wide-field cameras in the CT simulation room capture a full 3D surface of patients and their accessories. This includes the key collision risk areas, such as elbows and knees.
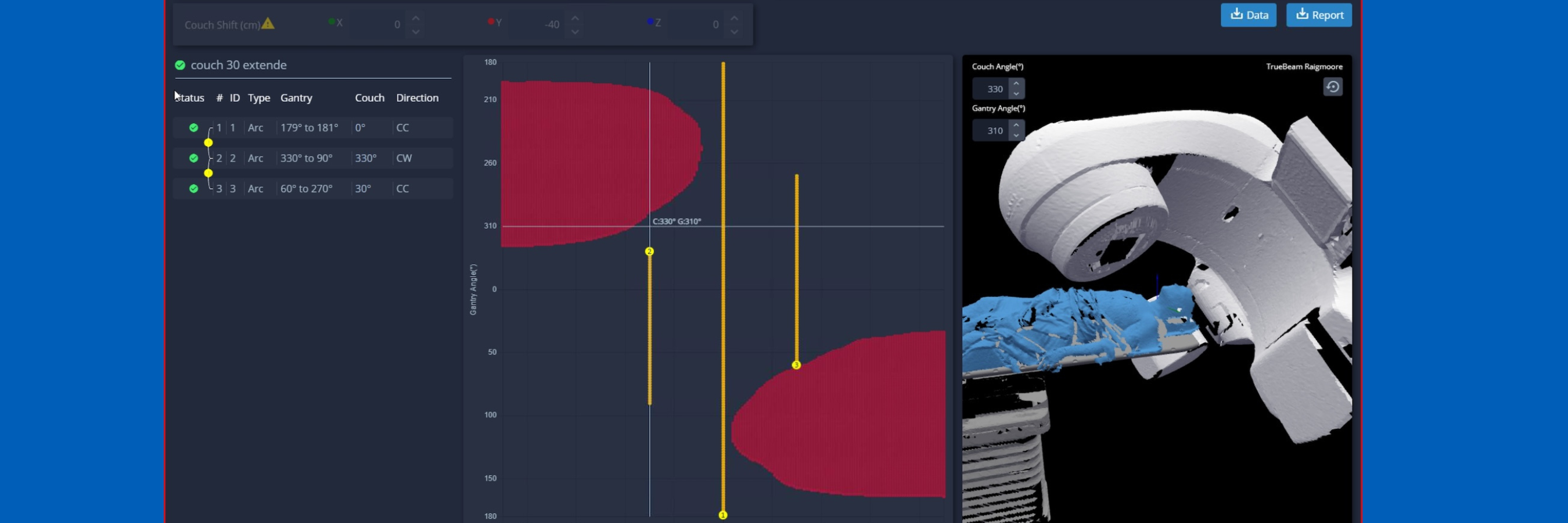
- This 3D surface is then used to make a “virtual treatment room”, and calculate a clearance map: which beams are safe, for every couch/gantry angle combination.
Published evidence shows that MapRT use can improve treatment plans in around 20% of cases27. Typical increases in treatment time for clinically meaningful OAR dose reductions are 30-50 seconds per fraction27,28.
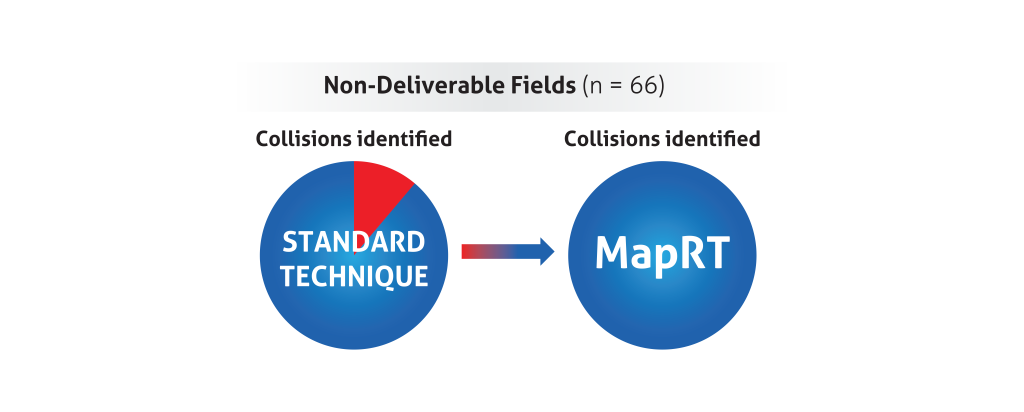
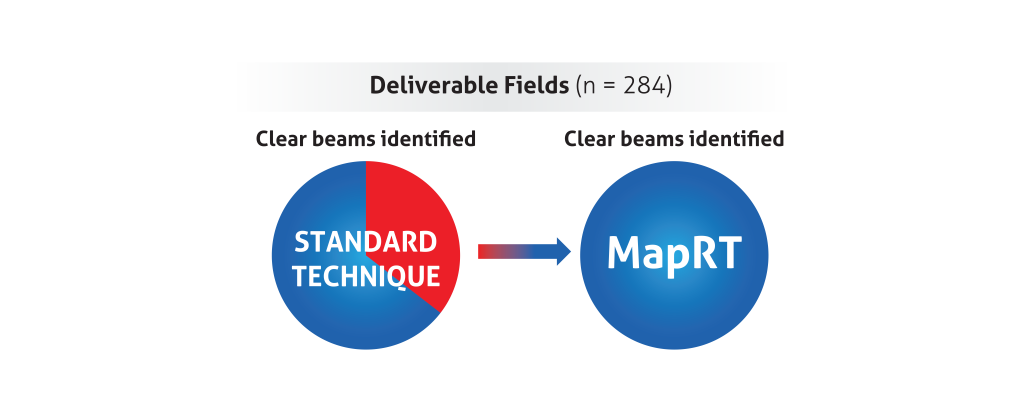
Improved assessment of deliverability
A five-center planning study29 recently showed improved assessment of deliverability using MapRT:
Modules to extend your MapRT system:
API Access in RayStation®
MapRT integrates directly with RayStation for collision checking and optimisation of non-coplanar beam angles.
API Access in Eclipse
MapRT clearance data can be accessed within Eclipse using the built-in Application Programming Interface (API).
Hear from users on their clinical experiences:
“I would say 30 more seconds of treatment in exchange for 4% of lifetime coronary event risk [reduction], I will take it.”
Siqiu Wang, Medical Physics Resident, University of Texas Southwestern
“From day one, you can ensure that any plan that you have has a safe delivery, and you can reduce your need for physical collision checks.”
Adi Robinson, PhD, DABR, AdventHealth Celebration
Eclipse™ is a registered trademark of Siemens Healthineers. The use of Eclipse™ here in is for identification purposes only.
Use of these marks does not indicate sponsorship, affiliation, endorsement or approval by Raysearch Laboratories or Siemens Healthineers.
MapRT uses exclusively licenced patents 62/128,906, 15/555,669, PCT/US2016/02023 4 and 16759347.4.
Frequently Asked Questions
Clinically meaningful plan improvements have been shown with only 30 seconds increase in treatment time2. Capturing the entire patient and accessory surface during simulation typically takes 1-2 minutes. Many users find MapRT helps avoid the work of physical clearance checks, and the new API enables clinics to access clearance data within their TPS.
RayStation 2025 (Photon) has a native integration with MapRT, allowing dynamic clearance checking during plan construction.
Multiple Eclipse users have scripts to view clearance maps and beam clearances inside the TPS.
The published evidence is strong that non-coplanar VMAT treatment are superior to standard VMAT. MapRT specific evidence includes a 900-patient study showing plan improvements in 18.4% of cases1, and a multicenter trial showing improved dose conformity and compactness which would not have been considered without MapRT.
Get in touch
Ready to take the next step?
Vision RT’s family of SGRT solutions guide radiation therapy for better patient care at every step: Sim, Planning, Treatment and Dose. Whether you’re looking for a quote, a product demo (virtual or in-person) or just more information, please get in touch.